Randomization ≠ Randomness | A Closer Look at Global Trial Scrutiny
International Clinical Trials Day 520 is just around the corner—Let’s take this opportunity to explore the evolution of clinical trials,starting with the cornerstone of modern study: randomization.
A Century of Science, A Legacy of Logic: The Birth of Randomization
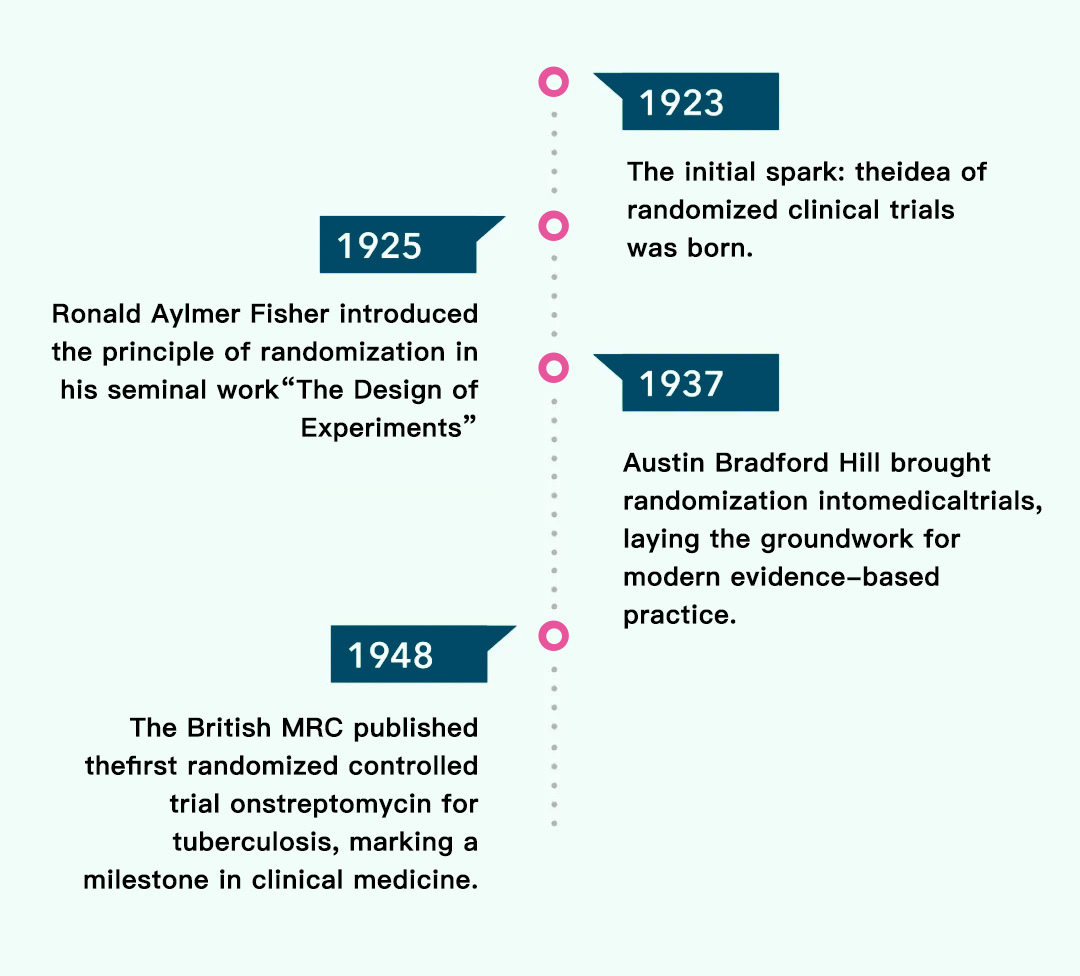
From concept to cornerstone, randomization has become one of the most essential elements in ensuring the credibility, comparability, and clarity of study outcomes. By distributing participants fairly and freely across treatment arms, it eliminates selection bias and enables scientific objectivity.
Randomization in a Regulated World: Spotlight on Global Compliance
In the evolving global regulatory landscape, randomization has consistently remained a core area of scrutiny. Major authorities including the FDA, EMA, MHRA, EU GMP, and ICH-GCP all provide clear guidance and requirements related to randomization practices.

For instance, the EMA’s 2023Reflection paper on the use of IRTdelivers a deep dive into the operationalrequirementsandraises crucial implementation checkpoints:
QA review and sign-off procedures?
What’s included in the audit trail?
URS and testing scripts for systemchange and iteration?
Scope and documentation of training records
Internal inspection and self-check mechanisms?
In this intricate landscape, experiencedsystemvendors with global trial exposure can help sponsors navigate cross-border compliance challenges and ensure data integrity from design to database lock.
From Principle to Practice:
The latestQualityVerificationPoints ofClinicalTrialDataManagement provides structured guidance on data inspection scope and focus areas, highlighting randomization as a critical review component. Both the randomizationprotocol and results are explicitly listed as “key inspection items.”
Description of randomization software & parameters
Measures to control bias?
Consideration of stratification factors?
Required components of the randomization protocol?
Ability to reproduce randomization outcomes?
Confirmation of the randomization process and individualrandom records
Release process for randomization lists
The group standard sets clear requirements for the trial's blinding, randomization personnel's blind status, random code generation software and parameters, randomization recurrence, and unblinding process. This provides crucial considerations for on-site inspections and effective research data evaluation.
ACCMED-IRT adheres to the industry's highest standards for process control, ensuring the accuracy and completeness of randomization. Key aspects include randomizationprotocols, parameter details, and recurrence. Additionally, it excels in blind status protection, drug management, and seamless offline-online collaboration, offering a powerful and user-friendly experience beyond expectations.
Randomization is not “random”– ACCMED-IRT Has You Covered
Execution matters. Challenges solved.
Stay tuned,ACCMED will be back with moreto talk!